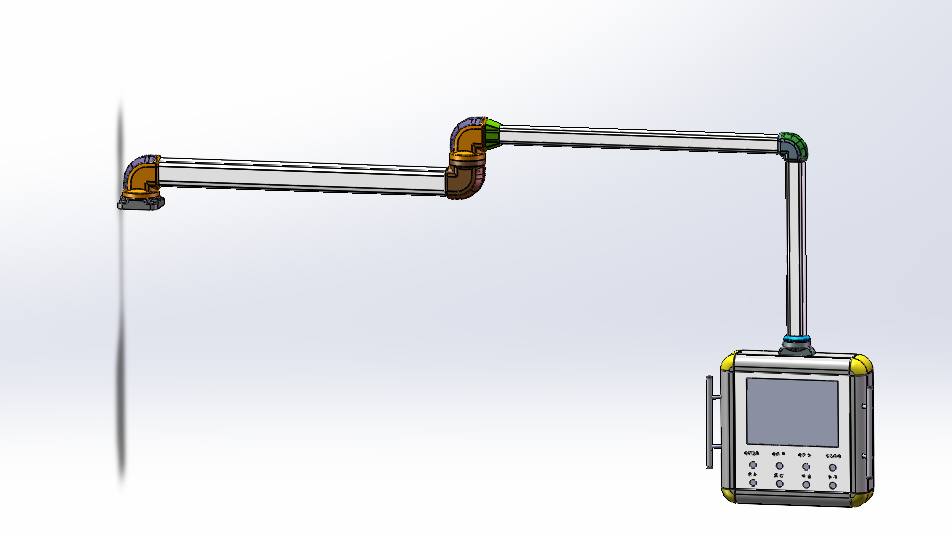
Functions of the Cantilever for Mechanical Power Control Box Assembly
The cantilever used for assembling mechanical power control boxes serves as a flexible ergonomic solution designed to support operator monitors or control interfaces. Unlike robotic arms, its primary role is to enable workers to adjust the position and angle of displays or control panels seamlessly during machine operation. Here are its core functions:
#### 1. **Flexible Adjustment of Operation Angles and Positions**
- **Multi-Directional Rotation**: The cantilever typically allows 360° horizontal rotation and vertical tilting (e.g., -45° to +45°), enabling operators to pivot the monitor to the optimal viewing angle based on their站位 (standing position) or workflow. This is critical for quickly checking parameters on the power control box, reading status indicators, or interacting with touch interfaces.
- ** Telescopic Adjustment**: With extendable arms, the monitor can be pulled closer for detailed operations (e.g., programming, troubleshooting) or pushed back to save space during routine monitoring. For example, an operator might extend the monitor to input parameters into the control box and retract it to observe overall equipment status from a distance.
#### 2. **Convenient Monitor Installation and Stabilization**
- **Compatibility with Multiple Displays**: Designed to fit various monitor sizes and types—from small monochrome screens to large color touchscreens—via standardized VESA mounts or adjustable clamps. This flexibility allows enterprises to select displays based on operational needs and budgets.
- **Stable Fixation**: Built with robust structures (e.g., aluminum alloy or steel) and anti-vibration mechanisms, the cantilever ensures the monitor remains secure even in high-vibration industrial environments. This prevents screen晃动 (shaking) or dislodging, maintaining clear visibility for accurate operation.
#### 3. **Space Optimization and Cable Management**
- **Desktop Space Saving**: By mounting the monitor on the cantilever, operators free up valuable workspace on control panels for tools, documents, or physical switches. This is especially beneficial in compact industrial settings, creating a tidier and more efficient layout.
- **Organized Cable Routing**: Integrated cable channels or clips within the arm guide power cords, signal cables, and USB lines neatly from the monitor to the control box. This reduces tangling, tripping hazards, and cable wear, while improving workplace safety and compliance with industrial hygiene standards.
#### 4. **Enhanced Operational Convenience and Efficiency**
- **Ergonomic Adaptability**: Operators can adjust the monitor’s height, angle, and distance to avoid awkward postures (e.g., neck strain from looking up/down), reducing fatigue during long shifts. This comfort directly improves focus and minimizes operational errors.
- **Quick, Tool-Free Adjustments**: Most cantilevers feature friction-based joints or quick-release mechanisms, allowing operators to reposition the monitor in seconds without tools. This agility is crucial for dynamic workflows, such as switching between machine monitoring and manual adjustments.
In summary, this cantilever optimizes human-machine interaction by prioritizing flexibility, stability, and ergonomic design. It streamlines operations in power control box assembly or maintenance, ensuring workers can access critical information efficiently while maintaining a safe, clutter-free workspace.